To get the maximal yield out of your crop, your sugar beets need to be treated with the uttermost care, because an optimal protection of your crop is of the highest priority. One of the biggest threats to your sugar beet field are pests and diseases.
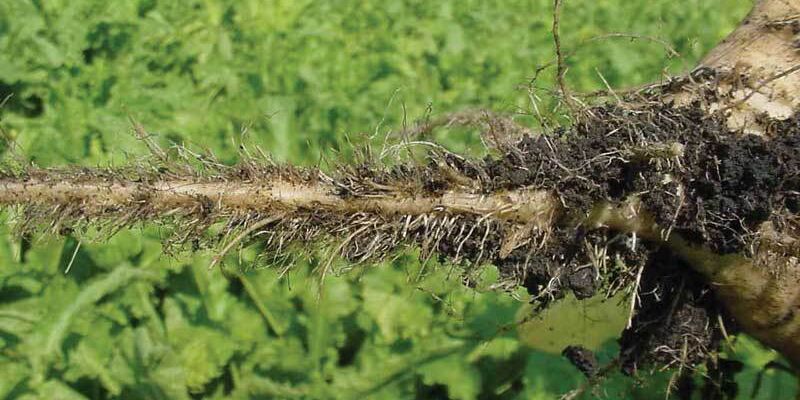
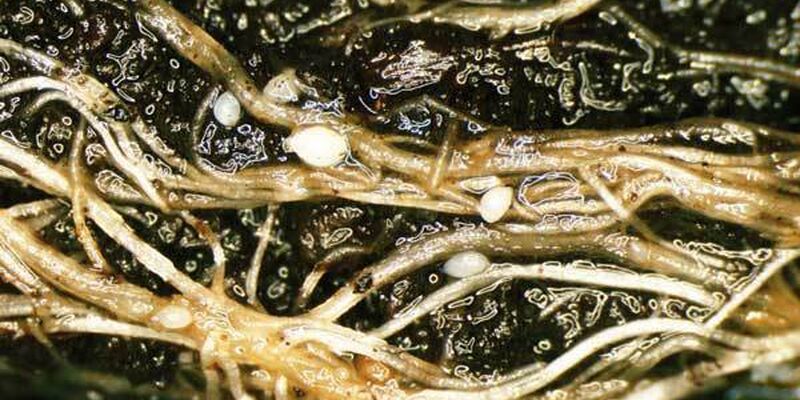


Nematodes
White beet cyst-nematode Heterodera schachtii is a white worm approximately 1 mm in length that can move through soil. It is capable of fixing itself onto the root of the sugar beet plant and feeding on the contents of its cells. This sometimes causes the proliferation of root hair to the detriment of the taproot.
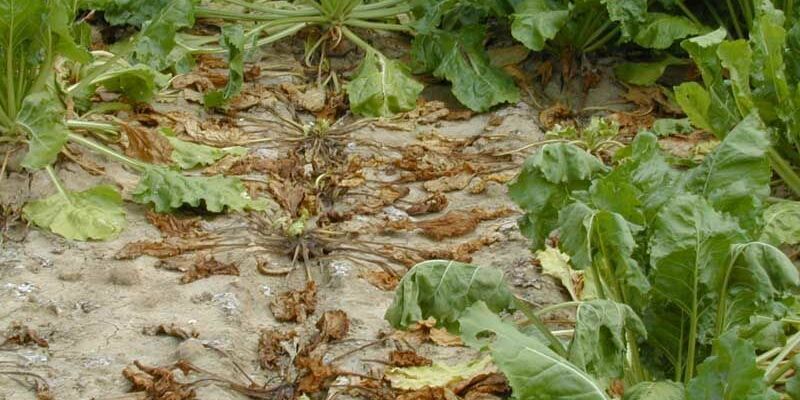
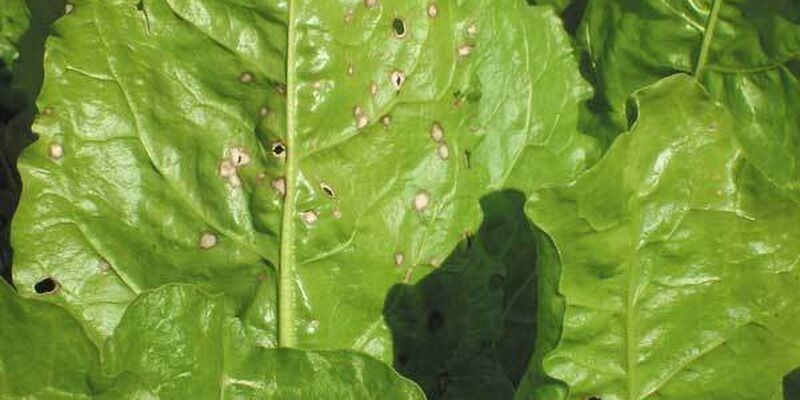


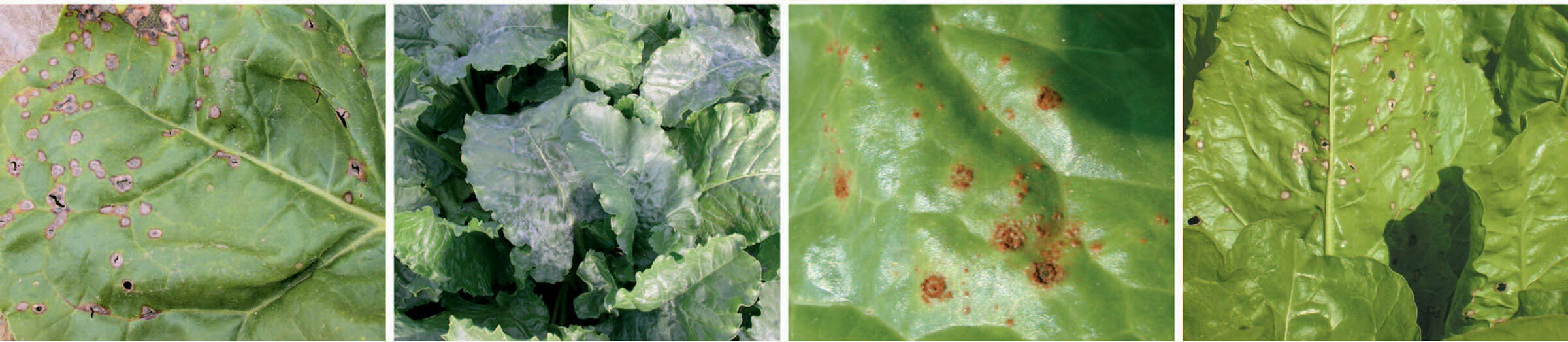
Leaf diseases
This category contains a series of diseases caused by fungi that attack the beet leaves. Their symptoms generally can be observed during the summer (in the beginning of the summer for cercospora leaf spot and powdery mildew; somewhat later for ramularia leaf spot and rust) until the harvest.